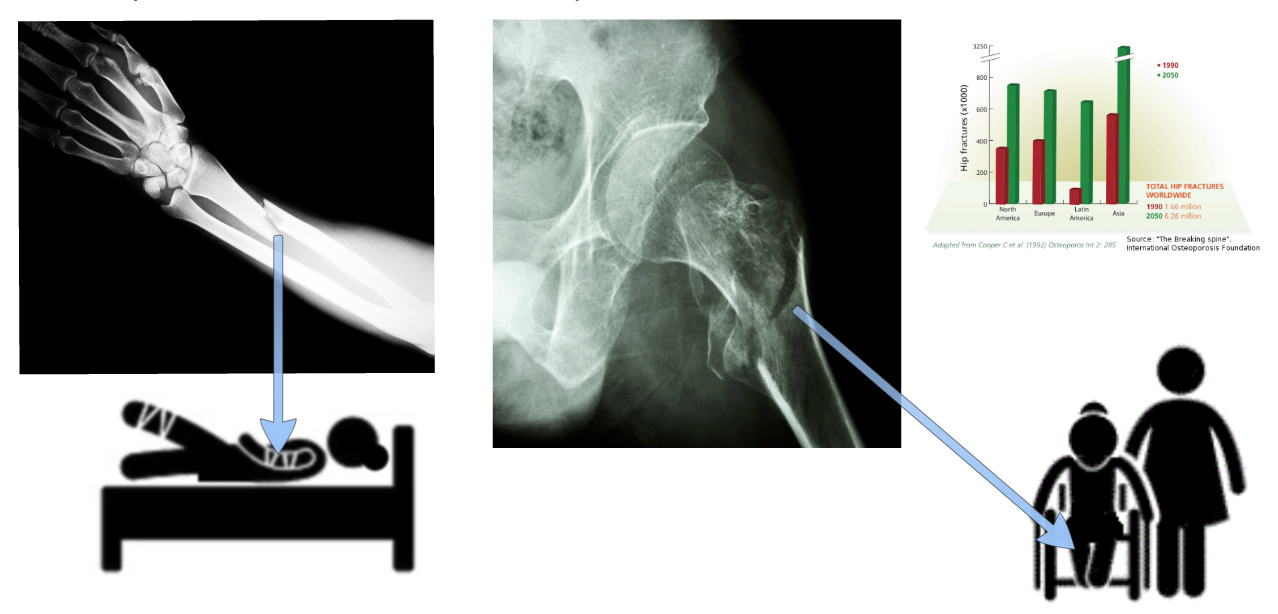
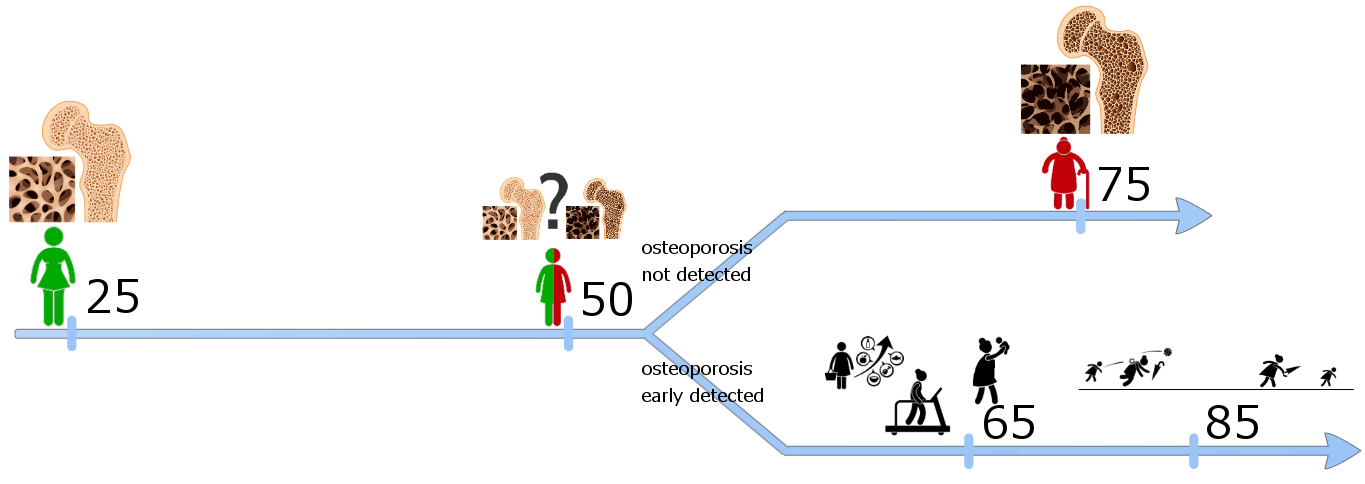
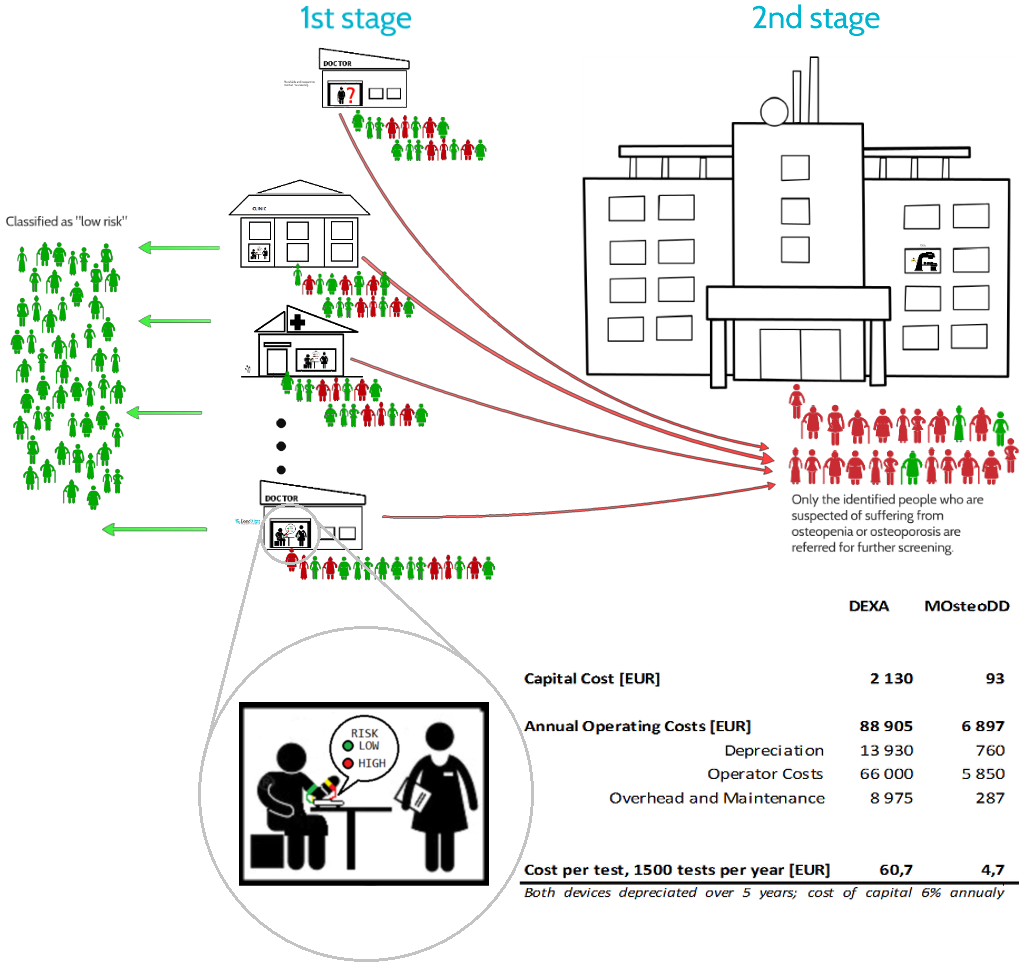
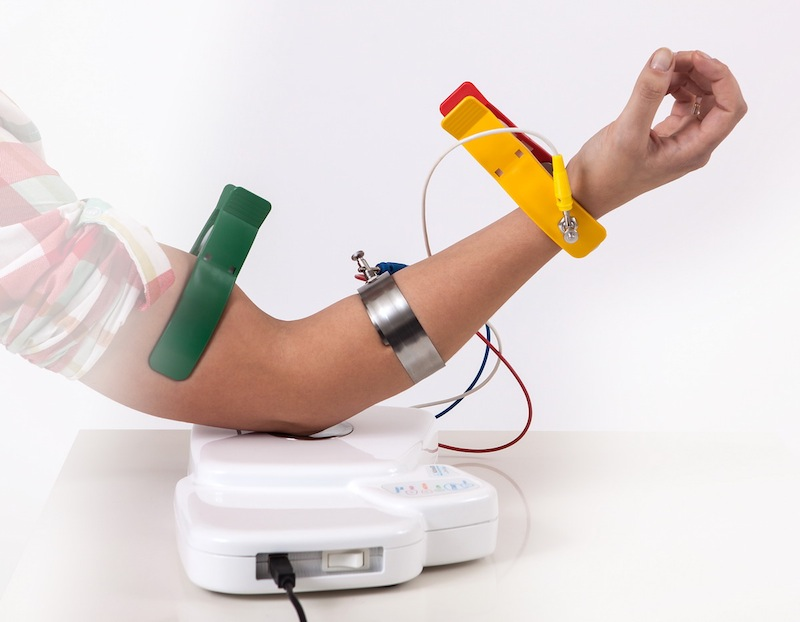
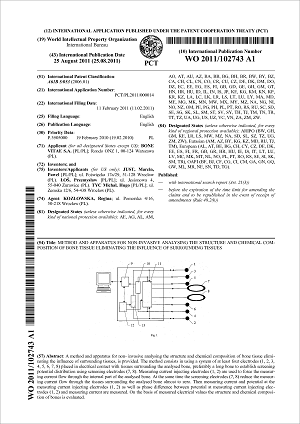
This Web page document (hereinafter referred to as the Presentation) contains information related to the Company BONE VITAE SA (hereinafter referred to as Company) and to the MOSTEODD, a newly invented device to detect early signs of osteoporosis. The presented information is not complete and has been prepared in order to provide potential investors with a basic knowledge of the Company, its product and opportunities for investment in the Company. The Presentation does not contain all the knowledge, which an investor might need to analyze investment opportunities. In any situation every investor should rely on his/her own research and analysis for any investment decision .
The Company has not declared explicitly or implicitly the accuracy, correctness and completeness of the information contained in this Presentation. The Company does not accept liability for any errors, mistakes and incomplete presentation and for possible damage suffered by an investor as a result of errors, mistakes and incomplete presentation. In addition, the Presentation may contain statements that are judgments, plan descriptions, intentions and projections relating to the future. The Company makes no representation that the submitted assessment shall be authorized, and the plans, intentions and projections are correct, and that they will be achieved. An investor should not rely on forward assessments, plans, descriptions of plans and projections without undergoing further independent analysis.
Distributing this Presentation, the Company reserves the right to supplement or amend it in part or in full at any time. This provision should not, however, be understood by an investor as the Company's obligation to submit changes, updates, additions or corrections to the presentation of the Company in the future. None of the new or changed information can be treated as correct or certain unless the Company clearly indicates otherwise.
The Presentation is not intended for free distribution. The Presentation contains information which is not publicly available, confidential and private, as a rule. An investor taking note of non-public confidential and private information contained in the Presentation accepts that the information will be treated by him/her in a confidential manner and that it will not be disclosed to any third party nor be reproduced, distributed, cited in any manner or for any purpose, without the written consent of the Company, except when the disclosure of confidential information is required by law or in relation to investor’s employees, who were informed of the confidential nature of the information and pledged to respect its privacy.